An Amper module is a directory with a module.yaml configuration file, and optionally sources and resources.
On this page
Introduction
Amper …
An Amper module is a directory with a module.yaml configuration file, and optionally sources and resources. A module configuration file describes what to produce: e.g. a reusable library or a platform-specific application.
Module layout
Here are typical module structures at a glance:
my-module/├─ resources/│ ╰─ logback.xml├─ src/│ ├─ main.kt│ ╰─ Util.java├─ test/│ ╰─ MainTest.java│ ╰─ UtilTest.kt├─ testResources/│ ╰─ logback-test.xml╰─ module.yamlAll sources and resources are optional: only the module.yaml file is required. For example, your module could get all its code from dependencies and have no src folder.
TODO: https://amper.org/latest/user-guide/basics/#module-file-anatomy
Working environment
Open the Idea editor and install the Amper plugin.
Create a “JVM console application” project:
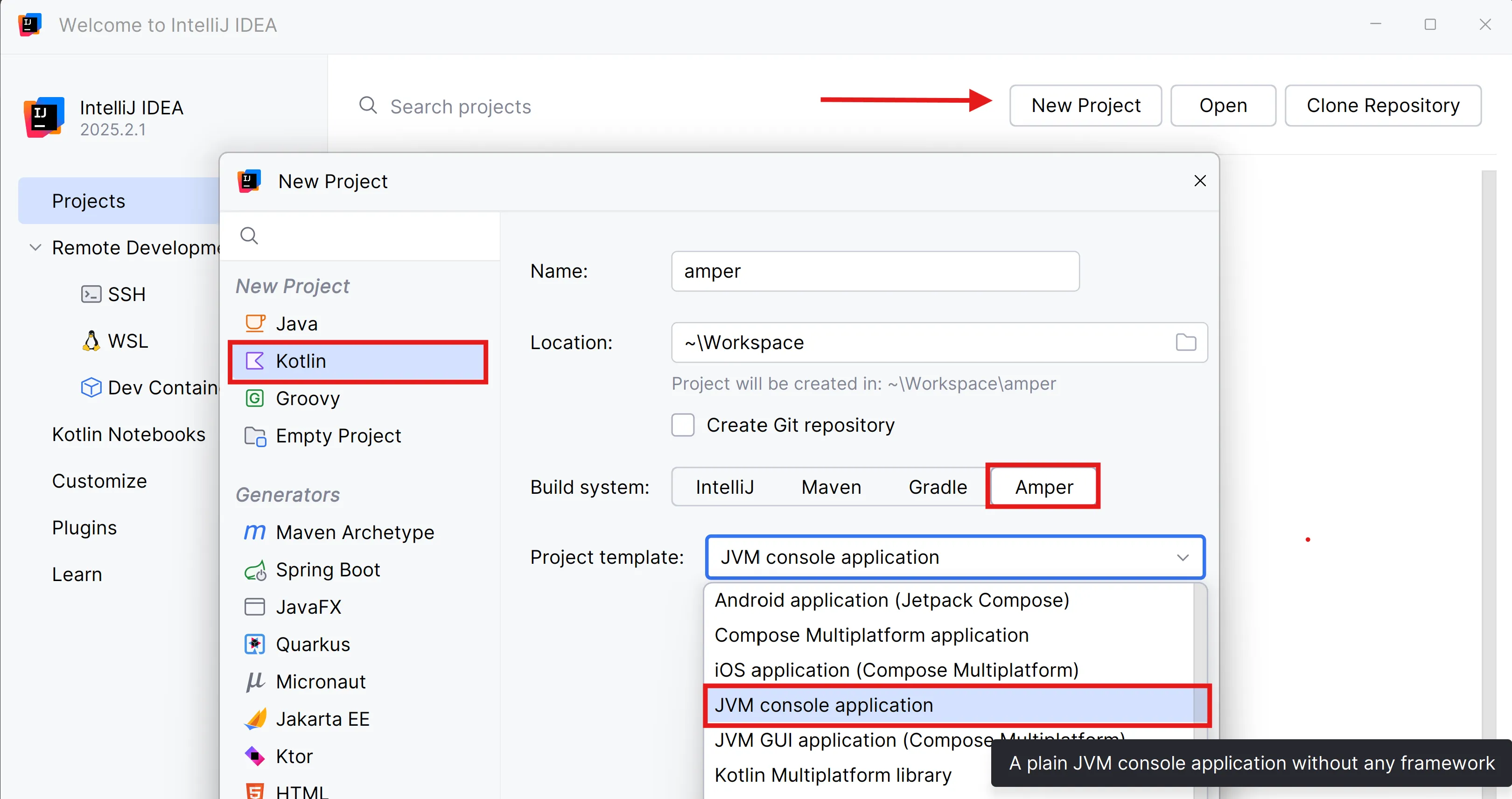
Module
An Amper module is a directory with a module.yaml configuration file, source files, and resources that describes a single product.
A module configuration file describes what to produce: for example, a reusable library or a specific application for desktop, Android, or other platforms.
Since you’ve created a simple JVM project, the content of the module.yaml file is minimal.
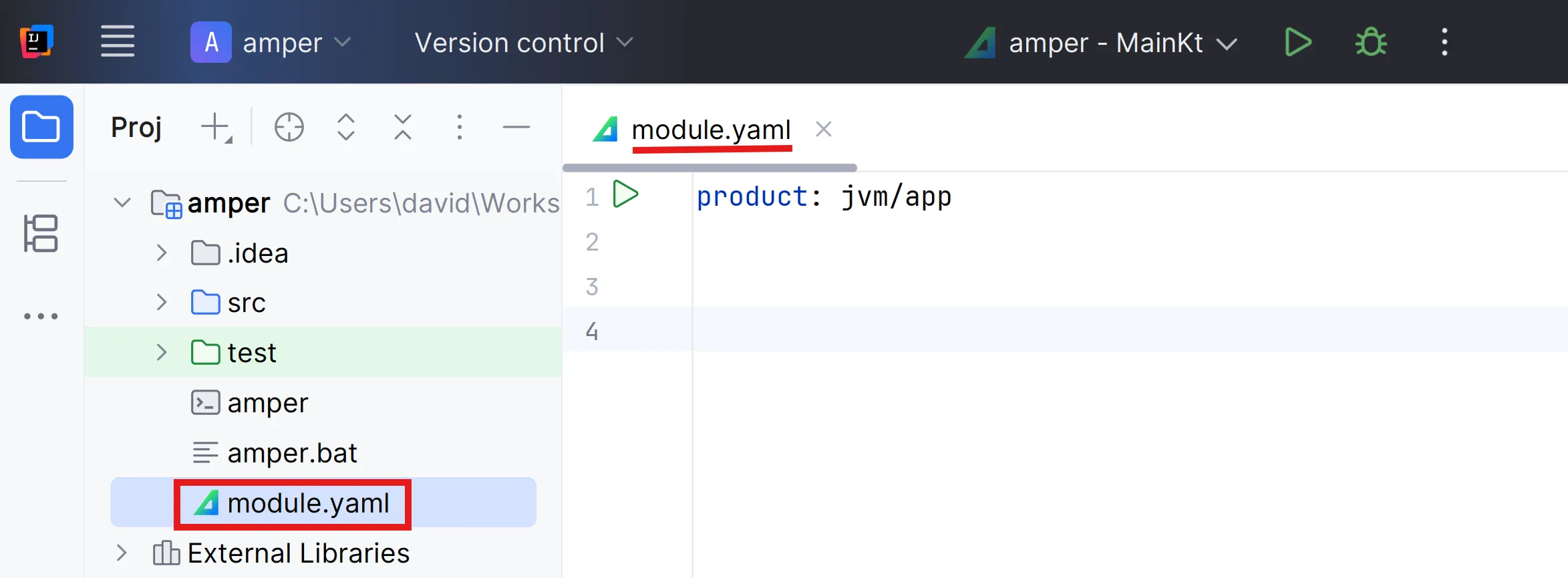
The file is in YAML format (check the activity if you don’t know what it is).
A module consists by default of the src and test folders.
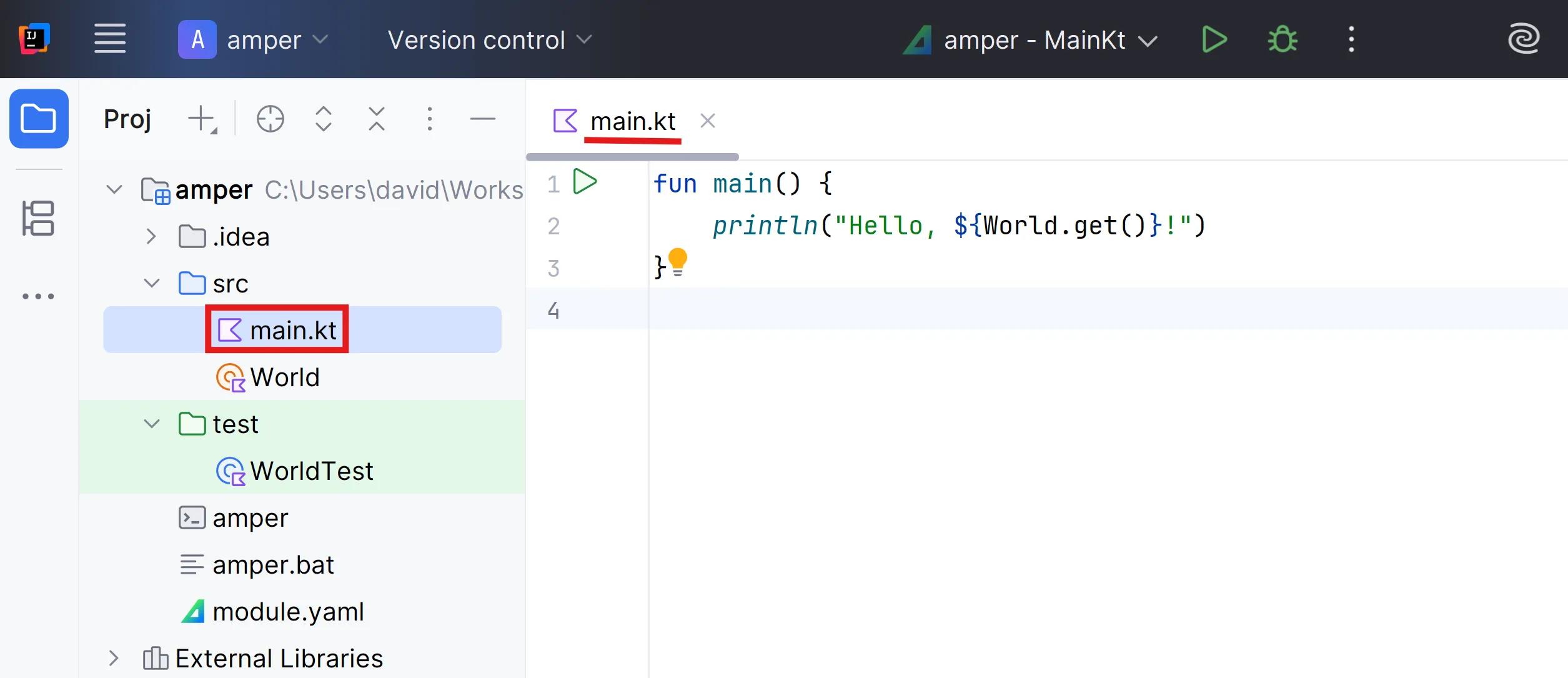
The main.kt and WorldTest.kt files are normal Kotlin files with nothing special.
To run an application, use the ‘run’ icon () next to the product section of the module.yaml file:
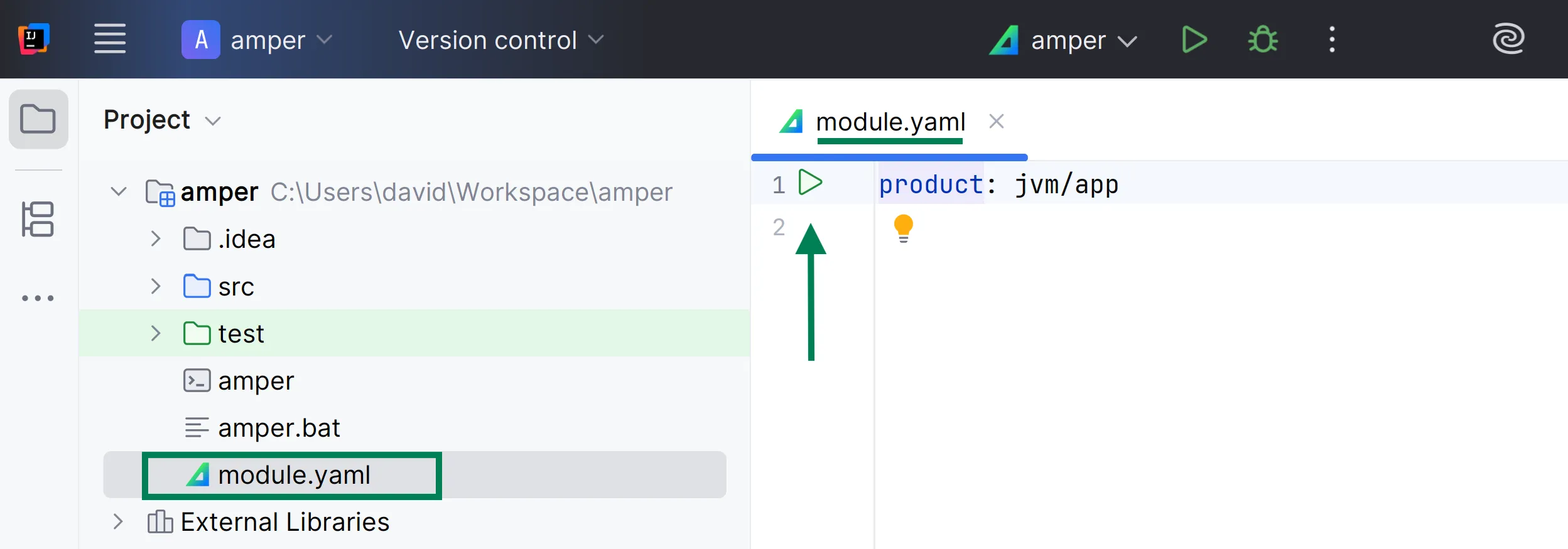
You can also use the ‘run’ icon ( ) next to the main() function:
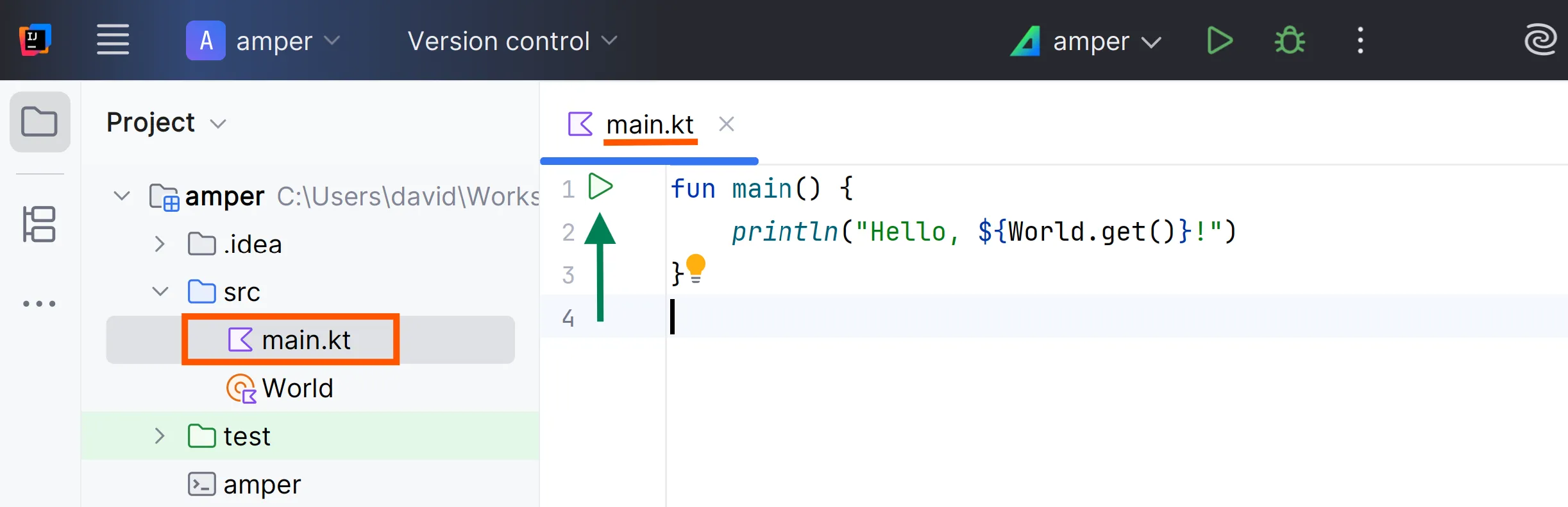
Source code
Source files are located in the src folder:
|-src/| |-main.kt|-module.yamlBy default, the entry point for JVM applications (the main function) is expected to be in a main.kt file (case-insensitive) in the src folder.
This can be overridden by specifying an explicit main class in the module configuration:
product: jvm/appsettings: jvm: mainClass: dev.xtec.TotoKtIn Kotlin, the main function is usually found at the top level of the file.
However, the JVM expects a main class when running any application.
Kotlin always compiles top-level declarations
into a class, and the name of this class is derived from the filename by capitalizing the name
and converting the .kt extension into a Kt suffix.
For example, top-level declarations from toto.kt will be in a class named TotoKt.
In a JVM module, you can mix Kotlin and Java source files:
|-src/| |-main.kt| |-Util.java|-module.yamlmodule.yaml
A module.yaml file has several main sections: product:, dependencies:, and settings:.
The product type describes both the target platform and the project type.
Below is the list of supported product types:
lib | A library that can be used as a dependency by other modules. |
jvm/app | A JVM console or desktop application |
jvm/lib | A library that can only be used on the JVM |
windows/app | A mingw64 application |
linux/app | A native Linux application |
macos/app | A native macOS application |
android/app | An Android VM application |
ios/app | An iOS/iPadOS application |
Here is an example of a JVM console application with a single dependency and a specified Kotlin language version:
product: jvm/appdependencies: - io.ktor:ktor-client-core:2.3.0settings: kotlin: languageVersion: 2.1CLI
When you create the project, the IDE downloads the latest versions of the amper scripts.
Open a terminal Alt + F12.
Update the Amper scripts and distribution to the latest published version.
They are likely updated, but in a project from a few months ago they definitely won’t be (this is how you learn).
.\amper updateYou don’t need to type .\amper.
It’s faster to type am and press the ⭾ key to autocomplete with .\amper.
The script is a small file that downloads and runs the actual Amper CLI distribution, and serves as an entry point for all Amper commands.
The first time you run the Amper script, it will take a while to download the Amper CLI distribution.
Subsequent runs will be faster, as the downloaded files will be cached locally.
*** Welcome to Amper v.0.8.0! ***
This is the first run of this version, so we need to download the actual Amper distribution.Please give us a few seconds now, subsequent runs will be faster.
Downloading Amper distribution v0.8.0...Download complete.
Downloading JetBrains Runtime v21.0.8b1038.68...Download complete.
Fetching latest Amper version info...Latest Amper version is 0.8.0Downloading Amper scripts...Download complete.Amper is already in version 0.8.0, nothing to updateTo run the src/main.kt file, you must run amper run:
.\amper runIf you don’t have an amper execution environment installed, it will download one for you automatically:
00:05.328 INFO :amper:compileJvm Downloading https://corretto.aws/downloads/resources/21.0.1.12.1/amazon-corretto-21.0.1.12.1-windows-x64-jdk.zip to C:\Users\david\AppData\Local\JetBrains\Amper\download.cache\5de2c13edf-amazon-corretto-21.0.1.12.1-windows-x64-jdk.zip00:21.241 INFO :amper:compileJvm Compiling module 'amper' for platform 'jvm'...Hello, World!00:25.140 INFO :amper:runJvm Process exited with exit code 0The ./amper command and all subcommands support the -h (or --help) option to explore what’s possible:
.\amper --helpUseful commands:
amper init | Create a new Amper project |
amper build | Compile and link all project code |
amper test | Run project tests |
amper run | Run the application |
amper clean | Remove build output and project caches |
Dependencies
A module needs many features that are not in the standard libraries.
You can search for libraries at MVN Repository.
We add a dependency on a Kotlin library from the Maven repository:
product: jvm/appdependencies: - org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-datetime:0.6.2Now you can use the kotlinx-datetime library in the main.kt file:
import kotlinx.datetime.*
fun main() { println("Hello, ${World.get()}!") println("It's ${Clock.System.now().toLocalDateTime(TimeZone.currentSystemDefault())} here")}For example, if I want to create charts, I can use the Kandy library.
Add a dependency on “Kandy”:
product: jvm/app
dependencies: - org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kandy-lets-plot:0.8.0 - org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-datetime:0.6.2Modify the main.kt file to create a bar chart:
import org.jetbrains.kotlinx.dataframe.api.*import org.jetbrains.kotlinx.kandy.dsl.*import org.jetbrains.kotlinx.kandy.letsplot.export.saveimport org.jetbrains.kotlinx.kandy.letsplot.layers.bars
fun main() {
val averageTemperature = dataFrameOf( "city" to listOf("New York", "London", "Berlin", "Yerevan", "Tokyo"), "average temperature" to listOf(12.5, 11.0, 9.6, 11.5, 16.0) )
averageTemperature.plot { bars { x("city") y("average temperature") { axis.name = "Average Temperature (°C)" } } }.save("plot.png", path = ".")}Run the application:
.\amper runOpen the plot.png file that has just been created.
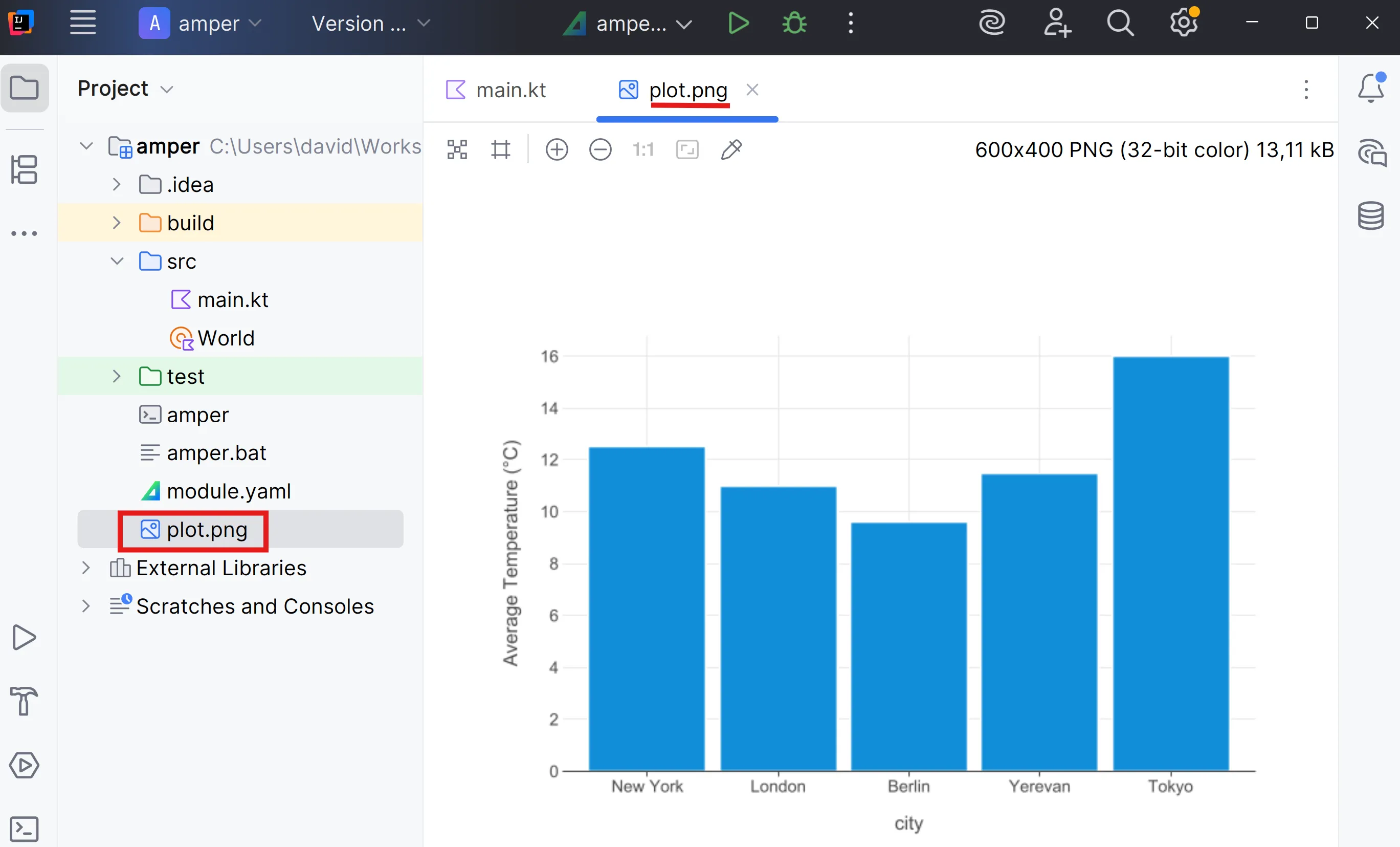
At any time you can see the project dependencies:
.\amper show dependenciesDependencies of module amper:
Module amper│ - main│ - scope = COMPILE│ - platforms = [jvm]├─── amper:main:org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kandy-lets-plot:0.8.0│ ╰─── org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kandy-lets-plot:0.8.0│ ├─── org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kandy-api:0.8.0.├─── amper:main:org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-datetime:0.6.2│ ╰─── org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-datetime:0.6.2 (*)╰─── amper:main:org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:2.2.10, implicit ╰─── org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:2.2.10 (*)Test
In Kotlin - Test you can learn how to manage test dependencies.
Compiler
Another typical task is configuring compiler parameters, such as the language level, etc.
For example, if you want the compiler to use compatibility with version 2.1 of the language, you can configure the settings section:
product: jvm/appsettings: kotlin: languageVersion: 2.1 # Set Kotlin source compatibility to 2.1In this link you have the different versions of the compiler available: Kotlin - Releases
If you feel like trying new versions of the Kotlin compiler before the next version of Amper, you can now customize the Kotlin compiler version with a simple configuration:
PENDING verification of operation 🤔
settings: kotlin: version: 2.3.0-Beta1Resources
Files placed in the resources folder are copied to the resulting products:
|-src/| |-...|-resources/ # These files are copied into the final products| |-...Package
Amper provides a package command to build a project for distribution.
For jvm/app modules it produces executable jars that follow The executable Jar format.
The executable JAR format, while commonly associated with Spring applications, is a universal packaging solution suitable for any JVM application.
This format provides a convenient self-contained executable deployment unit that includes all necessary dependencies, but unlike the shadow jar approach, it is devoid of duplicate processing issues.
Create an executable with amper package:
.\amper packageThe result is in the build/tasks folder.
If you have Java installed, you can run the application directly:
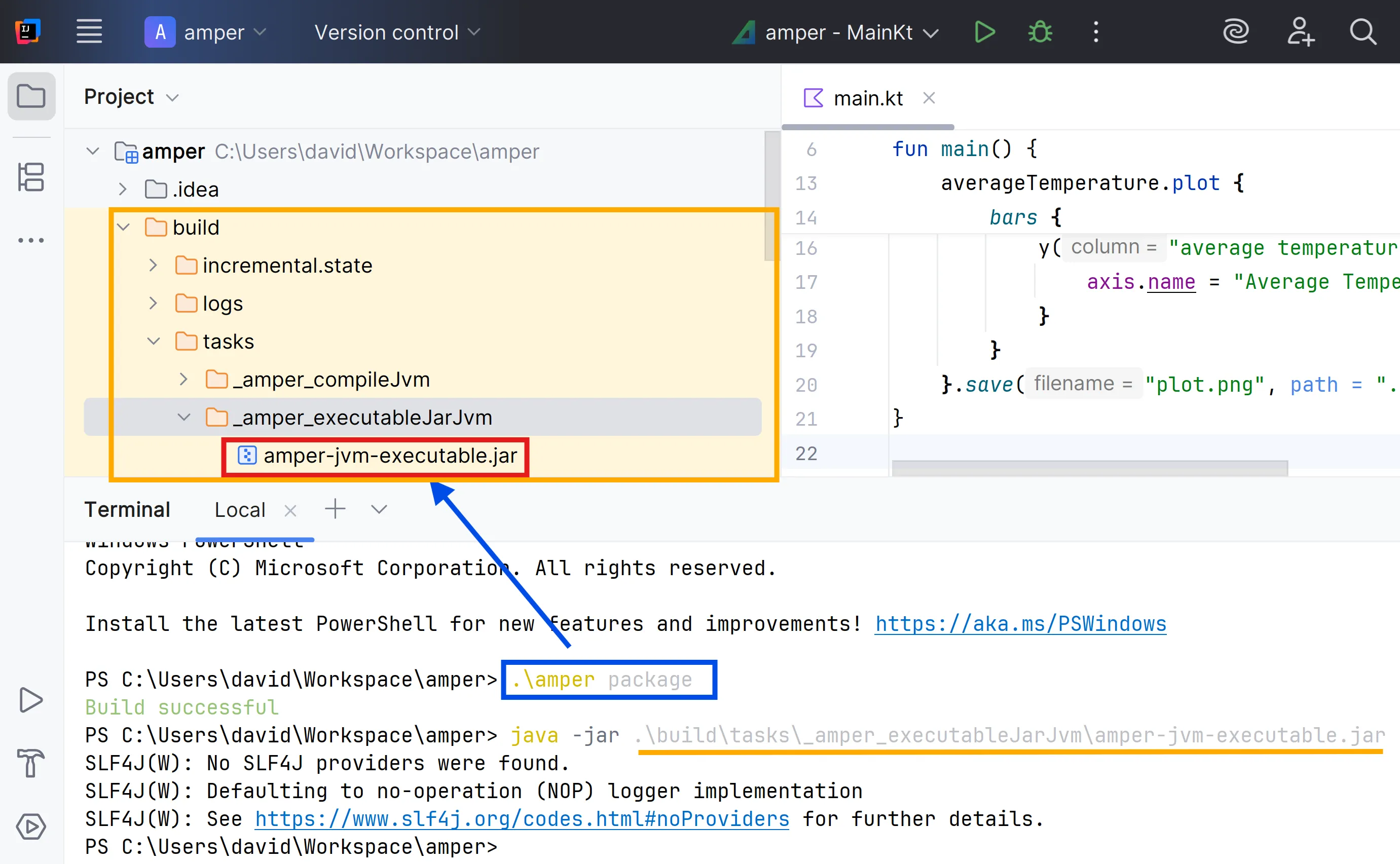
IDEA
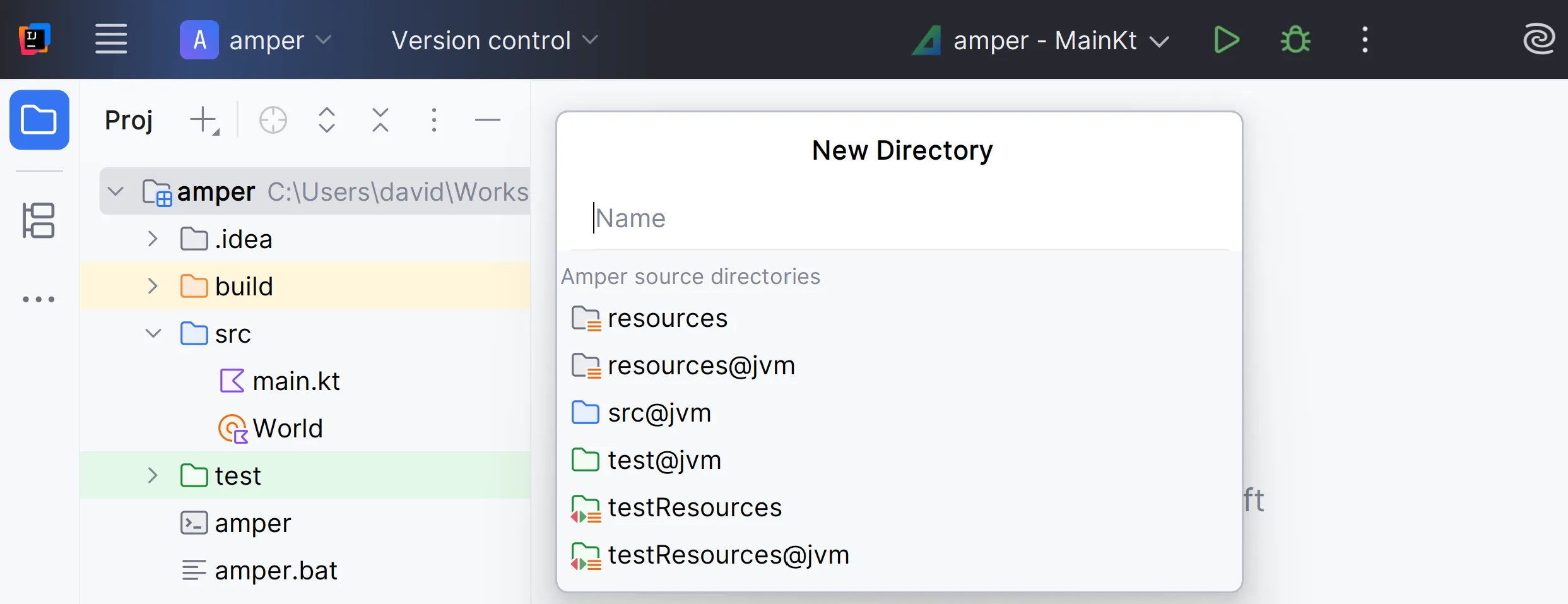
When you create new directories in an Amper module:
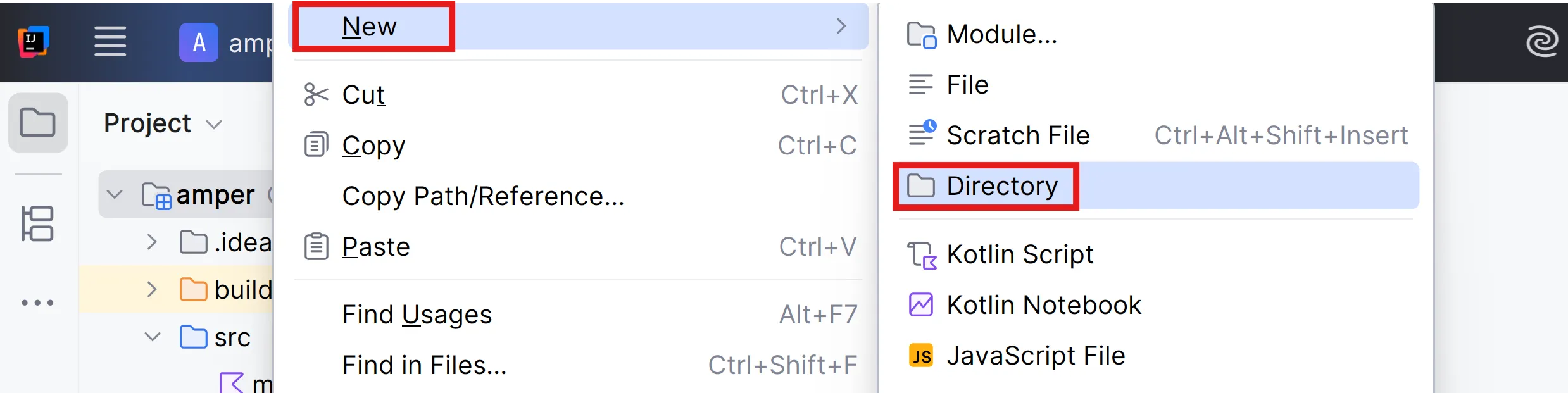
You can choose from several predefined options based on your platforms:
Activity
Create a small program that asks something from your user, does something, and shows the result.
Create a project that is distributable.