On this page
Introducció
Wireguard és aplicació que permet crear xarxes privades virtuals.
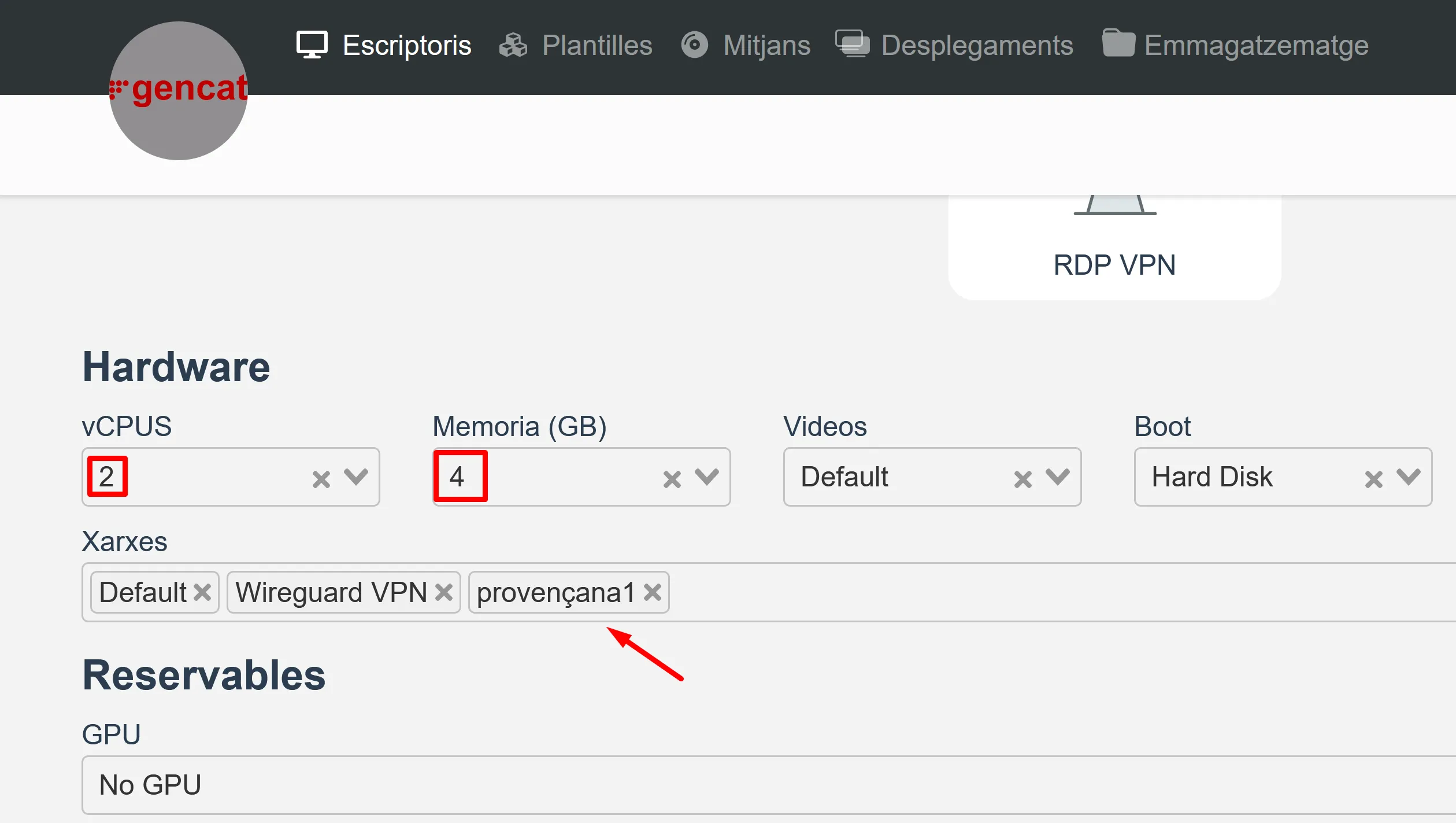
Crea tres màquines virtuals: box-1, box-2 i box-3 a Isard.
Les màquines han de ser “Ubuntu 24.04 Server” amb 2 CPU, 4 GB de RAM i una interfície de l’institut:
Connecta’t a la màquina box-1 amb ssh!
Activa les interfícies enp3s0 amb una IP fixa:
box-1$ sudo ip addr add dev enp3s0 10.0.0.101/24box-1$ sudo ip link set dev enp3s0 upFes el mateix amb box-2 (IP 10.0.0.102/24).
Verifica que pots fer ping des de box-1 a box-2:
box-1$ ping 10.0.0.102PING 10.0.0.102 (10.0.0.102) 56(84) bytes of data.64 bytes from 10.0.0.102: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.06 ms64 bytes from 10.0.0.102: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.09 ms^C--- 10.0.0.102 ping statistics ---4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 3004msrtt min/avg/max/mdev = 1.055/1.090/1.108/0.021 msEl primer pas és instal·lar WireGuard :
box-1$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y wireguardInterfície
Wireguard s’integra de manera completament transparent amb la resta d’elements del sistema perquè el que fa és crear interfícies virtuals que externament funcionen com qualsevol altra interfície física.
Afegeix una nova interfície mitjançant ip-link:
box-1$ sudo ip link add dev wg0 type wireguardPots veure que s’ha creat la interfície:
box1$ ip --brief addrlo UNKNOWN 127.0.0.1/8 ::1/128enp1s0 UP 192.168.123.21/22 metric 100 fe80::5054:ff:fe6d:dc1b/64enp2s0 UP 10.2.104.208/16 metric 100 fe80::5054:ff:fe6f:440e/64enp3s0 UP 10.0.0.101/24 fe80::5054:ff:fe28:e931/64wg0 DOWNXarxa
Una xarxa virtual funciona amb una xarxa IP privada.
Pots utilitzar la que vulguis, l’única condició és que no l’estigui fent servir una altra interfície.
Assigna una adreça IP privada a cada interfície amb ip-address:
box-1$ sudo ip addr add dev wg0 10.10.0.101/24box-1$ ip --brief addrlo UNKNOWN 127.0.0.1/8 ::1/128enp1s0 UP 192.168.123.21/22 metric 100 fe80::5054:ff:fe6d:dc1b/64enp2s0 UP 10.2.104.208/16 metric 100 fe80::5054:ff:fe6f:440e/64enp3s0 UP 10.0.0.101/24 fe80::5054:ff:fe28:e931/64wg0 DOWN 10.10.0.101/24Activa la interfície amb ip-link:
box-1$ sudo ip link set wg0 upVerifica amb ping que la IP privada funciona:
box-1$ ping 10.10.0.101PING 10.10.0.101 (10.10.0.101) 56(84) bytes of data.64 bytes from 10.10.0.101: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.033 ms64 bytes from 10.10.0.101: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.033 ms^C--- 10.10.0.101 ping statistics ---2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1036msrtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.033/0.033/0.033/0.000 msNginx
A continuació prova amb nginx que la interfície wg0 funciona sense problemes.
box-1$ sudo apt install -y nginxbox-1$ echo "box-1" | sudo tee /var/www/html/index.htmlVerifica que le servidor nginx funciona a la IP 10.10.0.101:
box-1$ curl 10.10.0.101box-1Xarxa
Una xarxa té sentit si hi ha més d’un node connectat.
Identitat
Wireguard fa servir criptografia asimètrica Curve25519
La clau pública permet identificar els diferents nodes de la xarxa virtual.
Amb wg pots generar claus privades:
box-1$ wg genkeygKwwK1zIljwcuNlWCo0nv4GJ9seARMX8B9h9+7Ph134=Configura la interfície wg0 una la clau privada:
box-1$ umask 077box-1$ wg genkey > keybox-1$ sudo wg set wg0 private-key keyAmb wg pots veure que la interfície wg0:
- Està configurada amb una clau pública que és el seu identificador.
- Un port aleatori on està escoltant:
box-1$ ~$ sudo wg showinterface: wg0 public key: XDx76G3NJ5vYzyi9SMge1z6lQV8Y+SWnKECidlThAi4= private key: (hidden) listening port: 54377Com ja saps, wireguard no necessita que li diguis quina és la clau pública, perquè tenint la clau privada pots generar la pública:
box-1$ wg pubkey < keyXDx76G3NJ5vYzyi9SMge1z6lQV8Y+SWnKECidlThAi4=Amb la comanda wg showconf pots saber quina és la clau privada:
box-1$ $ sudo wg showconf wg0[Interface]ListenPort = 54377PrivateKey = 6Ekvbq/UJFfspvZJHv4/9CPCVsh12s1uf/ADgHP83W8=Peer
Una interfície wireguard fa servir UDP (no es pot atacar amd DDOS) i és indetectable amb Network - Nmap.
Una interfície wireguard només respon a un paquet UDP si el remitent és un node de confiança.
Un node és de confiança si has registrat la seva clau pública com a un peer.
Per tant, configura la màquina box-2 amb una interfície wireguard:
box-2$ ip --brief addrlo UNKNOWN 127.0.0.1/8 ::1/128enp1s0 UP 192.168.122.110/22 metric 100 fe80::5054:ff:fe10:4957/64enp2s0 UP 10.2.145.44/16 metric 100 fe80::5054:ff:fe19:4915/64enp3s0 UP 10.0.0.102/24 fe80::5054:ff:fe64:1a66/64wg0 UNKNOWN 10.10.0.101/24La “id” d’un node és la seva clau pública.
Mira quina és la id de la interfície wg0 de box-2 i en quin port està escoltant:
box-2$ sudo wg show wg0interface: wg0 public key: YaCFmNYzvB8tl3wotX5Nx3HJMasJ1IQVnYyOncBZ0zs= private key: (hidden) listening port: 38240Ja pots configurar a box-2 com a peer de box-1:
box-1$ sudo wg set wg0 peer YaCFmNYzvB8tl3wotX5Nx3HJMasJ1IQVnYyOncBZ0zs= allowed-ips 10.10.0.102/32 endpoint 10.0.0.102:38240Fixa’t que has de dir a través de quina interfície real (endpoint) s’ha de crear la connexió virtual encriptada.
Pots veure que la interfície wg0 accepta connexions des de la IP 10.10.0.102.
box-1$ sudo wg show wg0interface: wg0 public key: XDx76G3NJ5vYzyi9SMge1z6lQV8Y+SWnKECidlThAi4= private key: (hidden) listening port: 54377
peer: YaCFmNYzvB8tl3wotX5Nx3HJMasJ1IQVnYyOncBZ0zs= endpoint: 10.0.0.102:38240 allowed ips: 10.10.0.102/32Ara configura box-1 com a peer de box-2:
box-2$ sudo wg set wg0 peer XDx76G3NJ5vYzyi9SMge1z6lQV8Y+SWnKECidlThAi4= allowed-ips 10.10.0.102/32 endpoint 10.0.0.101:54377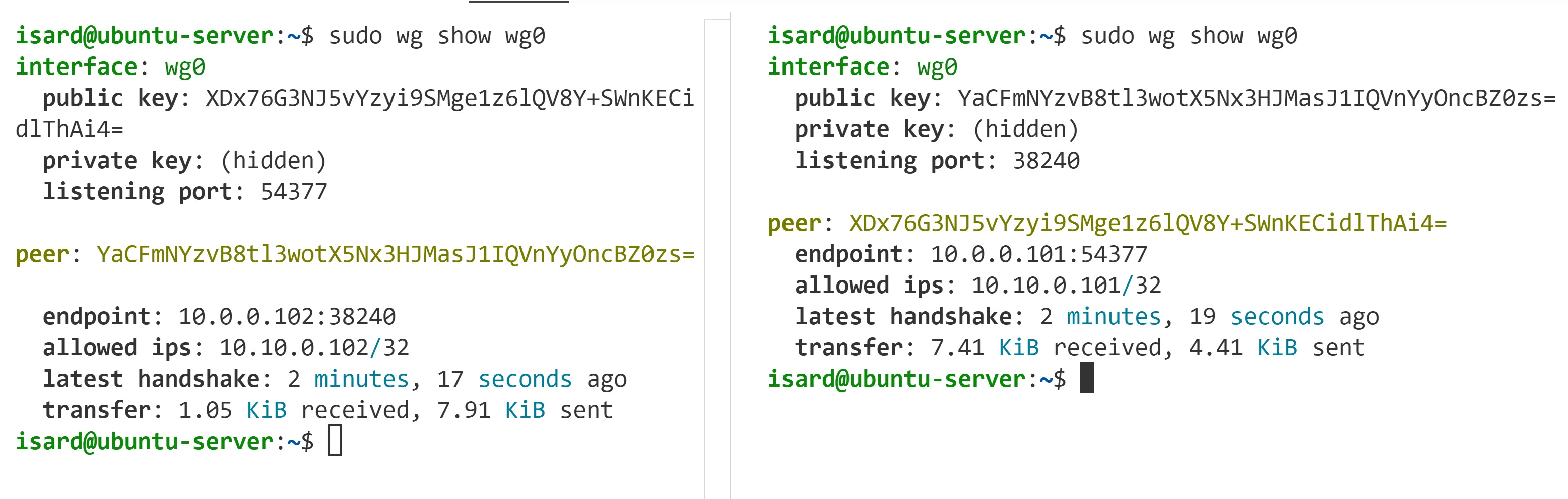
Ja pots fer ping de box-2 a box-1 a través de la interfície wg0:
$ ping 10.10.0.101PING 10.10.0.101 (10.10.0.101) 56(84) bytes of data.64 bytes from 10.10.0.101: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.020 ms64 bytes from 10.10.0.101: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.033 ms^C--- 10.10.0.101 ping statistics ---3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2081msrtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.020/0.029/0.034/0.006 msI al revés, de box-1 a box-2 a través de la interfície wg0.
L’ordre wg show et mostra que hi ha hagut tràfic en la interfície wg0:
box-2$ sudo wg show wg0interface: wg0 public key: YaCFmNYzvB8tl3wotX5Nx3HJMasJ1IQVnYyOncBZ0zs= private key: (hidden) listening port: 38240
peer: XDx76G3NJ5vYzyi9SMge1z6lQV8Y+SWnKECidlThAi4= endpoint: 10.0.0.101:54377 allowed ips: 10.10.0.101/32 latest handshake: 18 seconds ago transfer: 1.39 KiB received, 124 B sentPerò com pots estar segur que el peer està ben configurat?
Aixeca un servidor nginx a box-1 que respongui amb el seu nom:
box-1$ sudo apt install -y nginxbox-1$ echo "box-1" | sudo tee /var/www/html/index.htmlDes de box-2 verifica que et pots connectar al servidor nginx de box-1 des de la interfície enp2s0 i enp3s0:
box-2$ curl 10.0.0.101box-1box-2$ curl 10.10.0.101box-1Continua
Netplan
Genera les claus privada i pública en el primer peer. Executa les següents comandes amb privilegis d’administrador:
Generate the private and public keys in the first peer. Run the following commands with administrator privileges:
wg genkey > private.keywg pubkey < private.key > public.keyFes el mateix en el segon peer:
wg genkey > private.keywg pubkey < private.key > public.keyUtilitza la següent configuració en el primer peer (reemplaça les claus i les adreces IP segons sigui necessari):
network: tunnels: wg0: mode: wireguard port: 51820 key: UMjI9WbobURkCDh2RT8SRM5osFI7siiR/sPOuuTIDns= addresses: - 172.16.0.1/24 peers: - allowed-ips: [172.16.0.0/24] endpoint: 10.86.126.56:51820 keys: public: AIm+QeCoC23zInKASmhu6z/3iaT0R2IKraB7WwYB5ms=En el fitxer YAML anterior, key és la clau privada del primer peer i public és la clau pública del segon peer. endpoint és l’adreça IP del segon peer.
Utilitza la següent configuració en el segon peer:
network: tunnels: wg0: mode: wireguard port: 51820 key: UAmjvLDVuV384OWFJkmI4bG8AIAZAfV7LarshnV3+lc= addresses: - 172.16.0.2/24 peers: - allowed-ips: [172.16.0.0/24] endpoint: 10.86.126.40:51820 keys: public: EdNnZ1/2OJZ9HcScSVcwDVUsctCkKQ/xzjEyd3lZFFs=En el fitxer YAML anterior, key és la clau privada del segon peer i public és la clau pública del primer peer. endpoint és l’adreça IP del primer peer.
Debug
https://www.procustodibus.com/blog/2023/05/troubleshooting-wireguard-with-tcpdump/
sudo tcpdump -niany udp port 54377