Compose can be compiled to WebAssembly (Wasm) for use in modern browsers.
On this page
Introduction
With Kotlin, you have the power to build applications and reuse mobile and desktop user interfaces (UIs) in your web projects through Compose and Kotlin - Wasm.
For web platforms, Compose Multiplatform uses Kotlin/Wasm as its compilation target. Applications built with Kotlin/Wasm and Compose Multiplatform use a wasm-js target and run in browsers.
Explore this online demo of an application built with Compose Multiplatform and Kotlin/Wasm
Additionally, you can use the most popular Kotlin libraries in Kotlin/Wasm out of the box. Like in other Kotlin and Multiplatform projects, you can include dependency declarations in the build script.
Get started
Create a new project with the Web target and the Share UI.
Once the project loads, select composeApp [wasmJs] in the list of run configurations and click Run.
The web application opens automatically in your browser. Alternatively, you can open the following URL in your browser when the run is finished:
The port number can vary because the 8080 port may be unavailable. You can find the actual port number in the output of the Gradle build.
Gradle
You can run the wasmJsBrowserDevelopmentRun task to compile the project and open the HTML file in the browser.
.\gradlew wasmJsBrowserDevelopmentRunIf you prefer, you can use the --continuous flag to keep the browser open and automatically reload the page when you modify the code.
.\gradlew wasmJsBrowserDevelopmentRun --continuousGenerate artifacts
Generate your project’s artifacts to publish on a website:
./gradlew wasmJsBrowserDistributionThis will generate the final result in the composeApp/build/kotlin-webpack/wasmJs/productionExecutable directory.
You can use the files in this directory to deploy to any static web server.
Publish the application
Use the generated artifacts to deploy your Kotlin/Wasm application. Select a publishing option of your preference and follow the instructions to deploy the artifacts.
Some alternatives are:
- Gitlab - Pàgines
- Cloud - Netlify
- Cloudflare
Once your site is created, open the browser and navigate to your platform’s page domain.
Project structure
In the composeApp/build.gradle.kts file you have the Kotlin configuration with the “wasm” target:
kotlin { @OptIn(ExperimentalWasmDsl::class) wasmJs { // ...You also have the composeApp/src/wasmJsMain/resources/index.html file to load the wasm project and show it in the browser:
<script type="application/javascript" src="composeApp.js"></script>The script file name will depend on your project name.
Browser support
To run applications built with Kotlin/Wasm in a browser, your users need a browser version that supports WebAssembly’s garbage collection and legacy exception handling proposals. To check the browser support status, see the WebAssembly roadmap.
WebAssembly (Wasm) has also matured. As of December 11, 2024, all major browsers, including Safari, support WebAssembly Garbage Collection (WasmGC). This means Kotlin/Wasm applications can now run across all modern major browsers.
Improving the development experience for Wasm target has been our top priority. To that end, we’ve:
- Introduced incremental compilation, making builds up to twice as fast.
- Enhanced debugging support for browsers, providing better stepping functionality and an improved variable view.
Compatibility mode for Compose
We recommend targeting Wasm when you want an application with a multiplatform UI. However, there are some limitations to consider. The Wasm target relies on browser support for WasmGC, which may cause Kotlin applications targeting Wasm to be incompatible with older browsers that lack this support – see this guide for more details.
To address this, we’re introducing a compatibility mode in Compose Multiplatform.
-
With a new common source set called webMain, you will now have a single source for the
actualdeclarations for both JavaScript and Wasm targets. -
Using a special DSL in the CMP Gradle plugin, your application will be compiled to run the Wasm version of the app in modern browsers, taking full advantage of the Wasm target’s performance. For older browsers, the JavaScript version will run automatically, preventing a blank screen and maintaining usability.
Compose Multiplatform still relies on WebAssembly on the rendering engine side. However, this part uses WebAssembly features that have been available in all major browsers since 2017.
Present and Future of Kotlin for Web
kotlin-js-store
kotlin-js-store is a directory auto-generated by the Kotlin Gradle plugin to keep a lockfile for JavaScript dependencies — typically yarn.lock — so your builds use the exact same npm/Yarn dependency versions every time.
Why it exists
-
Kotlin/JS (and wasmJs) build rely on a Node/Yarn-based dependency graph (webpack tooling, JS libs, transitive packages).
-
The plugin puts the lockfile under kotlin-js-store/ to pin versions and prevents the “it worked yesterday, broke today” dependency drift.
Should you commit it?
In most teams, yes — treat it like any other lockfile: commit kotlin-js-store/yarn.lock to make CI and all developers resolve identical dependency versions. This is the whole point of having a lockfile.
Configuration
Incremental compilation
When working on Kotlin/Wasm projects, you may experience slow compilation times. This happens because the Kotlin/Wasm toolchain recompiles the entire codebase every time you make a change.
To mitigate this issue, Kotlin/Wasm targets support incremental compilation, which enables the compiler to recompile only those files relevant to changes from the last compilation.
Using incremental compilation reduces the compilation time. It doubles the development speed for now, with plans to improve it further in future releases.
In the current setup, incremental compilation for the Wasm targets is disabled by default. To enable it, add the following line to your project’s gradle.properties file:
kotlin.incremental.wasm=trueDebugging
Custom formatters have been added in the variable view. The implementation uses the custom formatters API, which is supported across major browsers like Firefox and Chromium-based ones.
With this change, you can now display and locate variable values in a more user-friendly and comprehensible manner.
Performance
Although Kotlin/Wasm is still in Beta, Compose Multiplatform running on Kotlin/Wasm already shows encouraging performance traits. You can see that its execution speed outperforms JavaScript and is approaching that of the JVM:
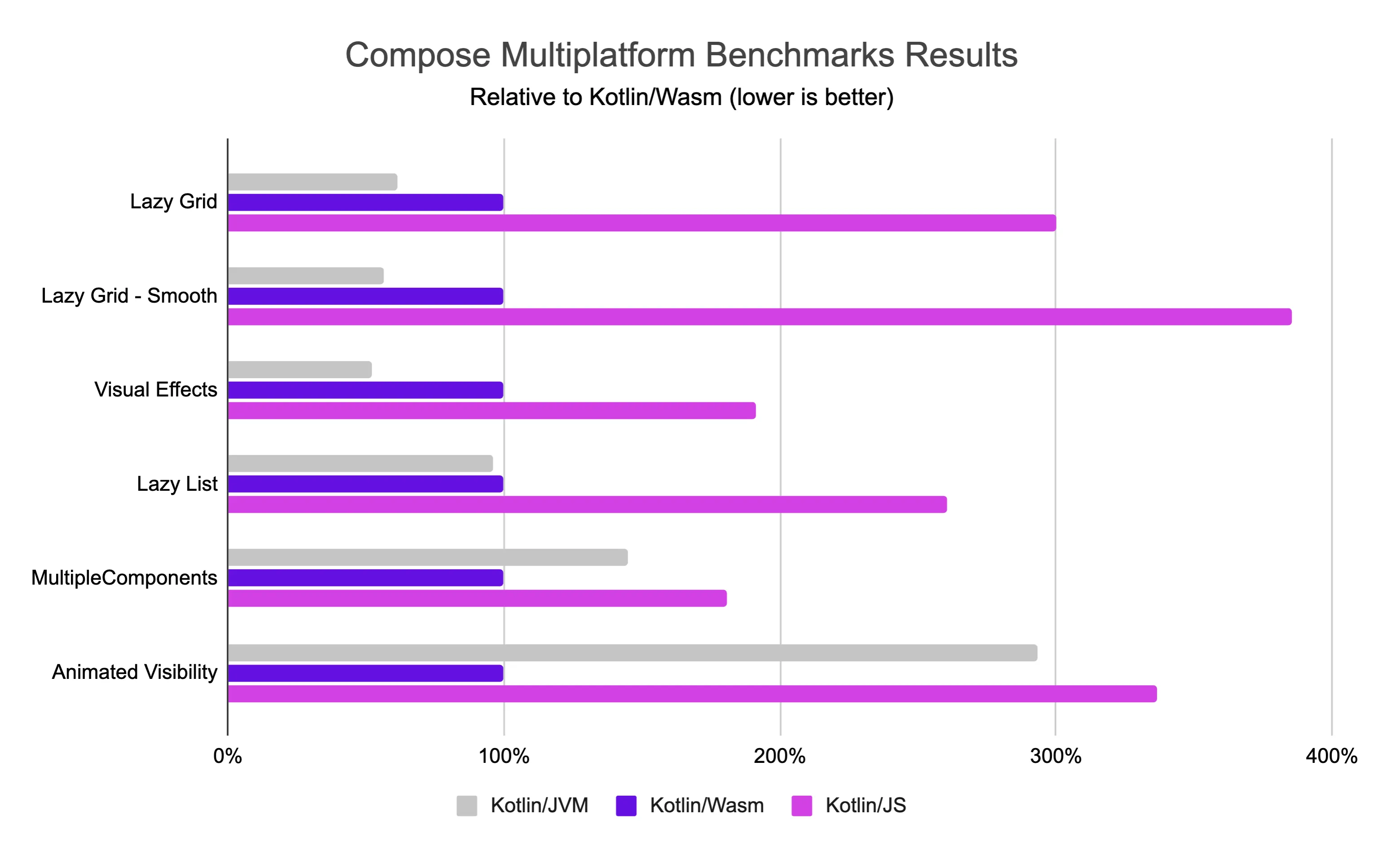
We regularly run benchmarks on Kotlin/Wasm, and these results come from our testing in a recent version of Google Chrome.
Browser API
The Kotlin/Wasm standard library provides declarations for browser APIs, including the DOM API. With these declarations, you can directly use the Kotlin API to access and utilize various browser functionalities. For example, in your Kotlin/Wasm applications, you can use manipulation with DOM elements or fetch the API without defining these declarations from scratch.
To learn more, see our Kotlin/Wasm browser example.
The declarations for browser API support are defined using JavaScript interoperability capabilities. You can use the same capabilities to define your own declarations. In addition, Kotlin/Wasm–JavaScript interoperability allows you to use Kotlin code from JavaScript. For more information, see Use Kotlin code in JavaScript.
Learn more
- Learn more about Kotlin/Wasm in this YouTube playlist.
- Explore the Kotlin/Wasm examples in our GitHub repository.